These tools and metrics are designed to help AI actors develop and use trustworthy AI systems and applications that respect human rights and are fair, transparent, explainable, robust, secure and safe.
Artificial Intelligence Forecasting System (AIFS)
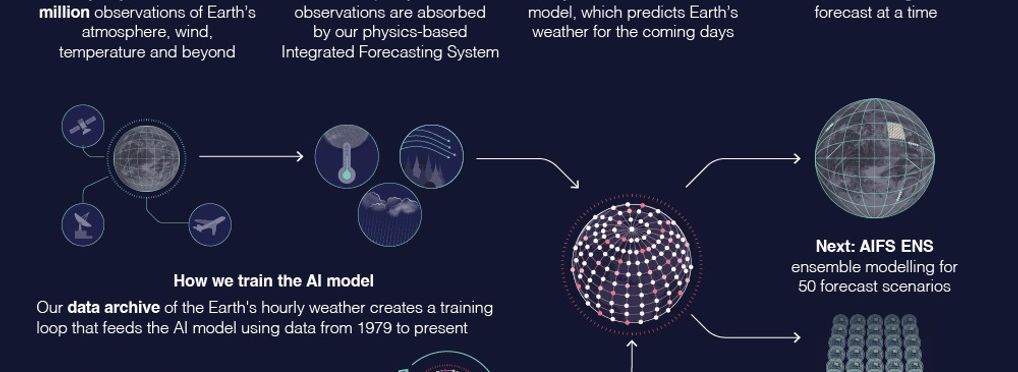
The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) officially launched the Artificial Intelligence Forecasting System (AIFS) into operational use alongside its physics-based Integrated Forecasting System (IFS) in February 2025.
The AIFS is the first fully operational weather prediction open model using machine learning technology for weather forecasting. It outperforms conventional models in key areas such as tropical cyclone tracking—improving accuracy by up to 20%. The AIFS is an open model which also users to use multiple fields including temperature, wind, and precipitation types. It leverages machine learning to provide faster, energy-efficient forecasts—reducing energy use by around 1,000 times compared to traditional methods.
AIFS uses the same initial data inputs as IFS, integrating over 60 million observations from satellites, aircraft, buoys, and ground stations every six hours. Unlike physics-based models that simulate weather via physical laws, AIFS predicts how the atmosphere will evolve based on learned patterns from historical weather data. Initially deployed as a single deterministic forecast system, AIFS will expand to ensemble forecasting—generating multiple forecast scenarios to better capture uncertainty. It holds strong potential across sectors like energy, insurance, shipping, and security, especially for medium-range planning.
The AIFS could potentially help industries where forecasts for the medium range can affect decision-making, such as the energy sector for pricing forecasts, as well as the insurance, security and shipping sectors.
In short:
- Observes: collects 800 million observations of the Earth's atmosphere, wind, temperature and other factors
- Absorbs: some of these observations are absorbed into the physics-based model Integrated Forecasting System. About 60 million quality-controlled observations are selected.
- Models: these observations are then used to feed the AIFS model;
- Predicts: and predicts the Earth's weather.
For more information visit the implementation of the AIFS operational model page and the AIFS blog posts.
About the tool
You can click on the links to see the associated tools
Developing organisation(s):
Tool type(s):
Objective(s):
Purpose(s):
Target sector(s):
Country/Territory of origin:
Type of approach:
Maturity:
Usage rights:
Target groups:
Target users:
Stakeholder group:
Geographical scope:
Tags:
- sustainable development
- geospatial information systems
- forecasting
Use Cases
Would you like to submit a use case for this tool?
If you have used this tool, we would love to know more about your experience.
Add use case



 Partnership on AI
Partnership on AI


























