The AI Workforce: What LinkedIn data reveals about ‘AI Talent’ trends in OECD.AI’s live data

LinkedIn’s Data for Impact programme’s collaboration with the OECD.AI Policy Observatory brings together the latest LinkedIn data on AI workforce trends to provide policymakers with information to understand the AI ecosystem better and make evidence-based decisions.
LinkedIn’s more than one billion members represent an economic graph that is a granular representation of the global economy updated in real time. While administrative systems can lag in updating taxonomies on AI occupations and skills, LinkedIn’s data identifies the latest trends in AI and the labour market.
LinkedIn’s latest methodology considers a member as AI engineering talent if they have explicitly added at least two AI Engineering Skills (see list below) – such as model training, AI agents, or large language models – to their profile and/or they are or have been employed in an AI job like an AI engineer. By capturing occupational and skills components, this refined definition represents the wider AI workforce more clearly and incorporates ongoing efforts to upskill and utilise AI across multiple sectors.
7 out of every 1,000 LinkedIn members globally have AI talent
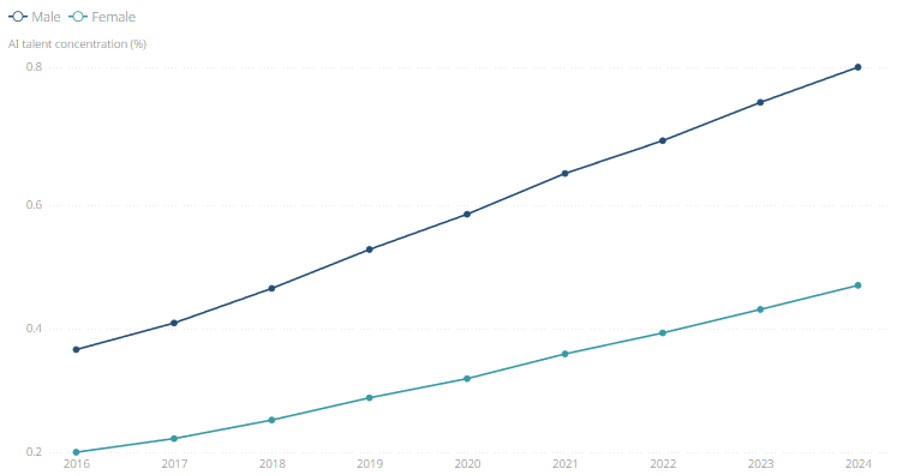
The AI workforce is growing at an unprecedented pace in response to the rapidly accelerating adoption of AI among employers. As of 2024, 7 out of every 1,000 LinkedIn members globally are considered AI engineering talent, representing a 130% increase since 2016. The highest concentrations of AI engineering talent are found in Israel (1.98%), Singapore (1.64%), and Luxembourg (1.45%). Furthermore, AI Literacy Skills (see list below), such as ChatGPT and Microsoft Copilot, grew by 600% in the last year.
Figure: Global AI engineering talent concentration of LinkedIn members by gender
AI adoption is not just in the Tech sector
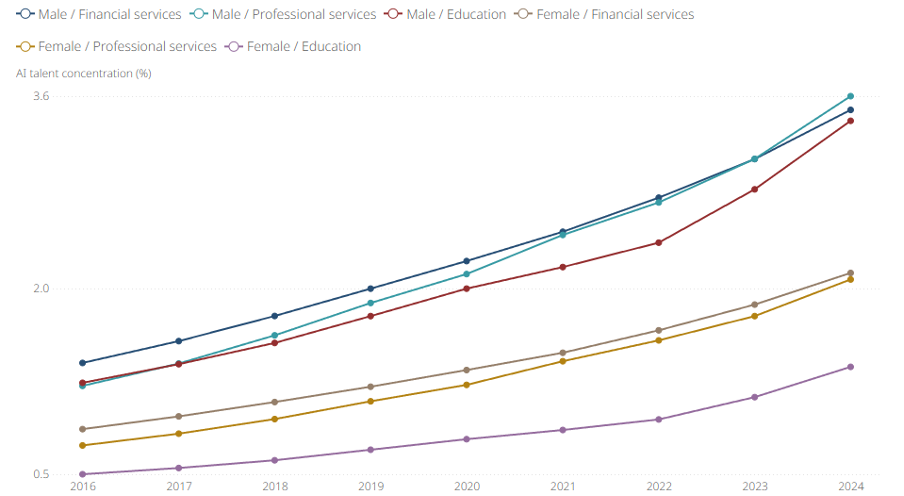
Increasing concentrations of AI talent across multiple industries demonstrate the widespread adoption of AI, not only in technology but also in professional services, financial services, and education. As AI talent develops across sectors, we also observe a persistent gender gap, although some industries seem better positioned to close it.
LinkedIn’s latest data on the AI gender gap reveals that in 2024, the share of men with AI Engineering Skills is 74% higher than the share of women with the same skills. This gap varies by industry; most industries analysed have a smaller gender gap than the 74% average.[CW5] One notable exception is education, where the AI gender gap is more than double the average, despite the industry having better representation of women. We also observe a gender gap in AI Literacy Skills, with the share of men possessing these skills being 138% greater than women. LinkedIn’s research on gender gaps within STEM further examines potential drivers of these disparities and their changes over time globally.
Figure: Global AI engineering talent concentration of LinkedIn members by industry and gender
Skill sets are adapting
As workers collectively seek to leverage this emerging technology, we observe skill sets evolving across the workforce. Understanding which skills are critical for leveraging AI, where those skills currently reside, and how to distribute them more evenly across the workforce may soon underpin countries’ economic growth and resilience.
The fastest-growing AI skills added by LinkedIn members in 2024 were Custom GPTs, AI Productivity, and AI Agents, reflecting AI’s broader shift in focus to GenAI and its use as a productivity tool. We also see strategic AI skills growing, such as AI Strategy (#7) and Responsible AI (#8), suggesting the evolution of a more mature AI ecosystem and a focus on policymaking.
Table: The fastest growing AI Skills (as defined by LinkedIn) added by LinkedIn members in OECD countries in 2024
| AI Engineering Skills | AI Literacy Skills | |
| 1 | Custom GPTs | Generative AI Tools |
| 2 | AI Productivity | Anthropic Claude |
| 3 | AI Agents | Microsoft Copilot Studio |
| 4 | Azure AI Studio | Microsoft Copilot |
| 5 | Amazon Bedrock | AI Prompting |
| 6 | OpenAI API | LLaMA |
| 7 | AI Strategy | Google Gemini |
| 8 | Responsible AI | Generative AI Studio |
| 9 | LangChain | GitHub Copilot |
| 10 | Computational Intelligence | AI Builder |
📊 See data about the fastest-growing AI Literacy Skills and AI Engineering Skills 📊
Data that pinpoints AI skill gaps
The latest 2024 LinkedIn data from OECD.AI offers a glimpse into the evolving landscape of AI skills and occupations, as well as the demographic dynamics of this workforce. LinkedIn’s methodology and definition of AI talent help pinpoint skills gaps and align workforce development with industry demands. Employers, workers, and policymakers can utilise this data and these methodologies to keep pace with the ever-changing nature of AI-related jobs and skills.

































